Tagging Files
To enable Cartographer to generate documentation from your codebase, you’ll need to tag the files you want it to process. Tagging is a simple, lightweight way to indicate which files or sections of code should be included in your documentation. Tags are added as a comment at the top of your code and consist of comma-separated values. Note: All attributes must stay on one line.
Required attributes- id: Must be between 4 and 30 characters and unique within your organization. This external ID is used by Cartographer to link documentation internally. If no document with external ID exists in your organization, it will be created.
- name: A human-readable title for the document.
- diagramType: Specifies the type of diagram to include; options include component, flowchart, or sequence diagram. Defaults to none.
- context: Allows you to add additional descriptive context to enhance the generated documentation.
- folderId: Assigns the document to a specific folder. If the folder does not exist, the document will be placed at the root level.
- spaceId: Although the space ID is typically set in your CI/CD pipeline, you may override it here to place the document in a different space if needed.
Using Multiple Files for a Single Document
In most projects, code is distributed across multiple files to maintain structure and readability. Cartographer supports this by allowing you to link several related files together and generate a single, cohesive document. This ensures your documentation accurately reflects how your code is organized and functions across modules.
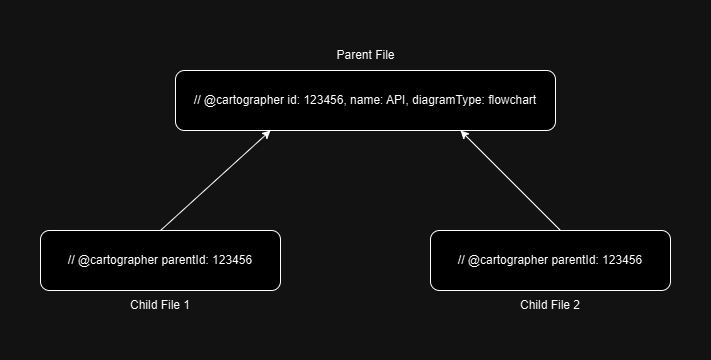
In the primary (or parent) file, add the standard tag as described above. To include additional related files, tag them using the following format:
If your parent file has an id of 123456,
you would use that value as the parentId in any
additional files you want to associate with the same document. You do
not need to add any additional attributes to child tags.